Twisted tube is a kind of enhanced heat transfer tubes that firstly presented by Swedish Alards Company, and then improved by the USA’ Koch Heat Transfer Company, LP.
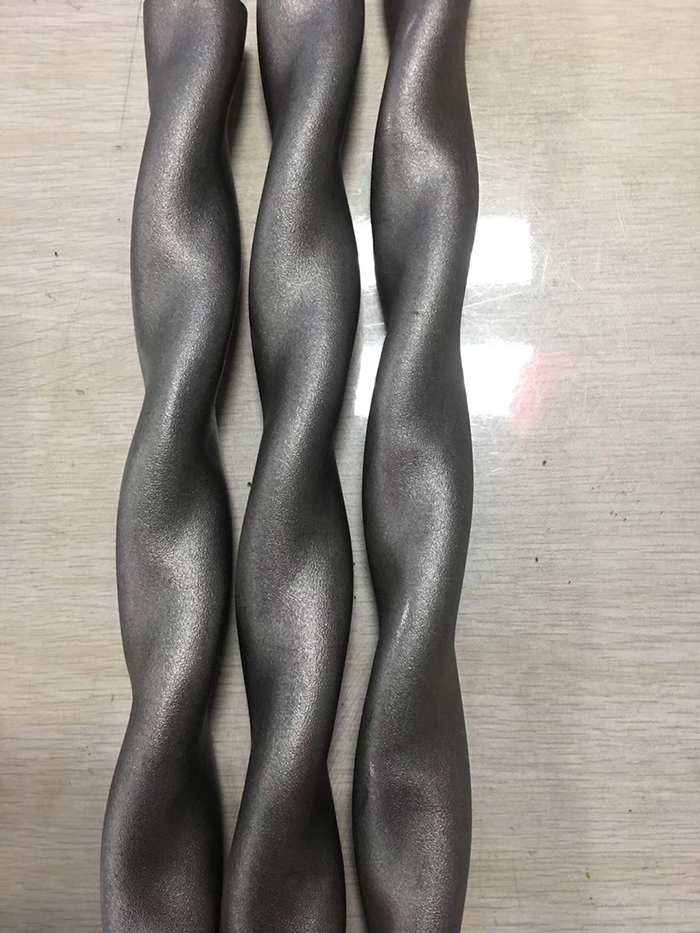
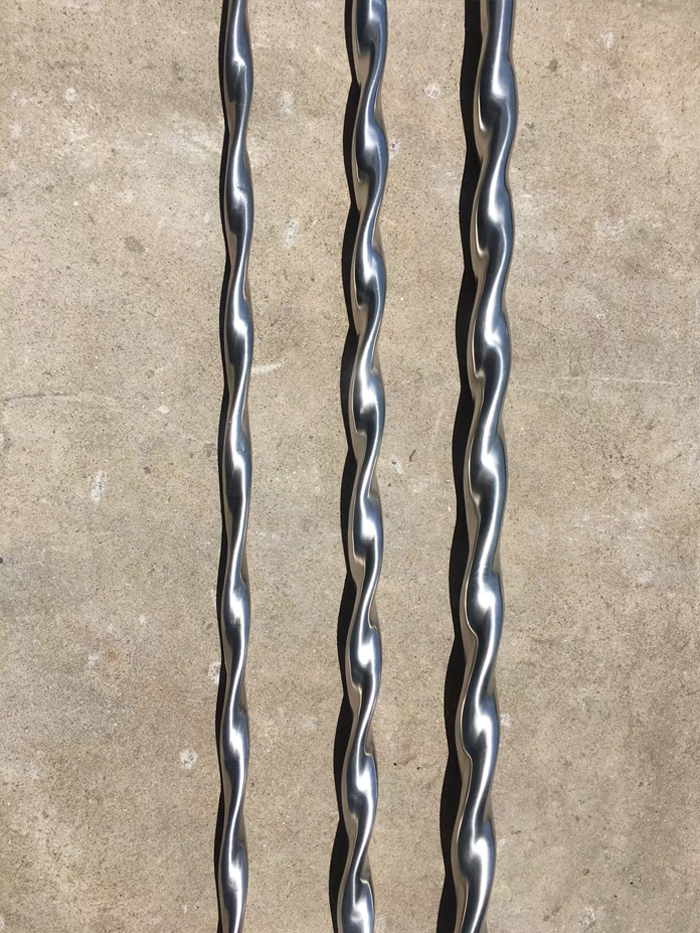
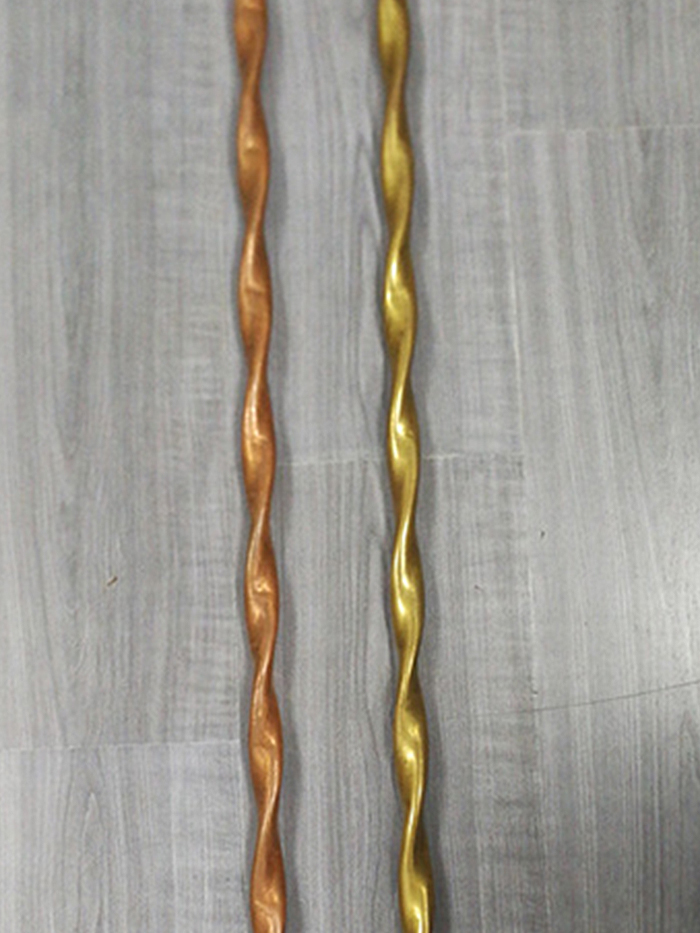



Fig. Twisted tube
1. Structure and manufacture of twisted tube
Structure and manufacture of twisted tube
The manufacturing process of twisted tube includes:"partial pressure" and "distortion". The tube’s cross section is nearly an ellipse, of which the ratio of long axis and short axis is designed according to the flow velocity in tube passes and shell passes of heat transfer tubes. When the flow rate in tube pass is low, the ratio of the long axis and short axis shall be increased, or the flow surface shall be reduced in order to increase the flow rate.
2. Enhanced heat transfer principles of twisted tube
The unique structure of twisted tube can make the flow in tube pass and shell pass in the spiral motion at the same time, by this way it enhanced the turbulent intensity. The heat transfer coefficient of the twisted tube is 40% higher than the normal one, but the pressure drop are almost same.
3. Advantages of heat transfer with twisted tube
| 1 | Lower pressure drop | No baffle plate, lower pressure drop in the shell pass |
| 2 | Higher heat transfer efficiency | It can increase the turbulent intensity, make the shell flow velocity and the direction change regularly, and enhance the mixture in lengthways |
| 3 | Less deposit | No blind zone in the shell |
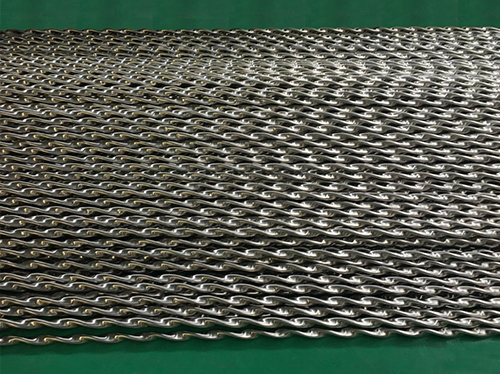


Fig. Stereogram of Stainless steel twisted tube



Fig. Brass, copper twisted tube



Fig. Carbon steel twisted tube
Seamless steel twisted tubes used for producing heat exchangers are complete ones without joints. Common materials used in steel tubes shows in bellow chart.
Tab. Material of tube
| Type | No. | Standard | Supply condition |
| Carbon steel | 10、20 | GB/T 9948-2006 GB/T 6479-2000 GB/T 8163-2000 | Annealed condition |
| Nickel | |||
| Titanium | |||
| Alloy of copper | |||
| Austenitic stainless steel | 0Cr18Ni9 | GB/T 13296-2002 GB/T 14976-2002 | Pickling & passivation |
| 00Cr19Ni10 | |||
| 0Cr18Ni10Ti | |||
| 0Cr17Ni12Mo2 | |||
| 00Cr17Ni14Mo2 |
4. Specification of twisted tube
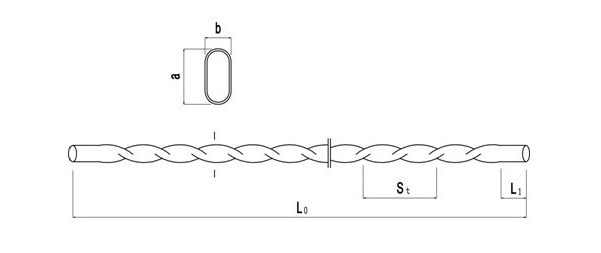
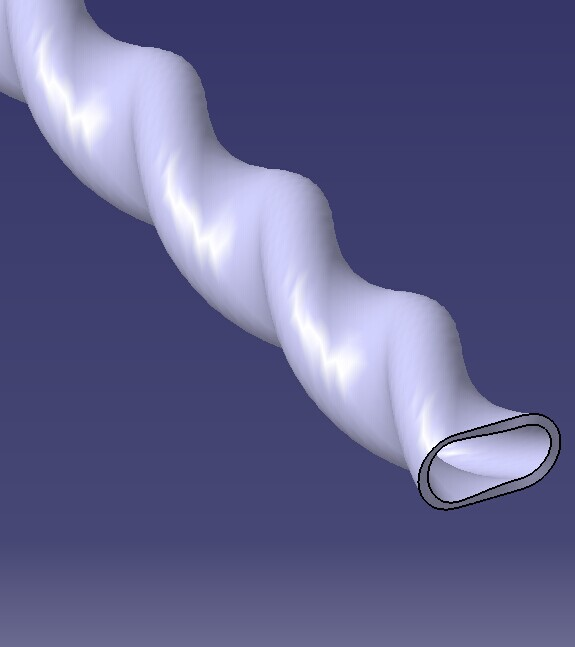
Fig. Basic dimension parameter figure of twisted tube
Tab. Basic parameter of twisted tube
| Spec. | Lead St(mm) | Long axis a (mm) | Short axis b (mm) | Length of bare ends L1 (mm) |
| Φ8 | 200 | Arbitrary length | ||
| Φ16 | 200 | Arbitrary length | ||
| Φ19 | 200 | 23.0 | 13.0 | Arbitrary length |
| Φ25 | 200 | 30.5 | 15.5 | Arbitrary length |
| Φ32 | 200 | 37.0 | 22.5 | Arbitrary length |
| Φ38 | 200 | Arbitrary length |
Note: The above table is the basic parameter of standard twisted tube. Twisted tube can be manufactured as the St and L, if there are special requirements.
5. Application of the Twisted tube
As twisted tube has been fast developed and improved in recent years, it is much more reliable and effective, which can almost be used in all kinds of shell and tube heat exchangers. More than 1000 twisted tube heat exchangers have been used since 1984, which can be used in gas-gas, liquid-liquid and liquid-gas heat transfer process, including chemistry, petroleum, food, papermaking, electric power, metallurgy, mining, and urban heating industries.